LEPIDIUM
Lepidium
L., Sp. Pl. 643. 1753; Gen. Pl. ed. 5: 291. 1754; Benth. & Hook. f., Gen. Pl. 1(1): 87.1862; Hook. F., Fl. Brit. India 1: 154.1875; Boiss., Fl. Or.1:353.1867; Thellung, Mitt. Bot. Mus. Univ. Zurich 28: 1-340. 1906; Schulz in Engl. & Prantl, Pflanzenfam. ed. 2, 17 b: 407. 1936; Fl. China@ eFloras.org 8: 28; Al-Shehbaz & Gaskin, Fl. North Amer. @ eFloras.org 7: 570; Fl. Pak. @ eFloras.org.
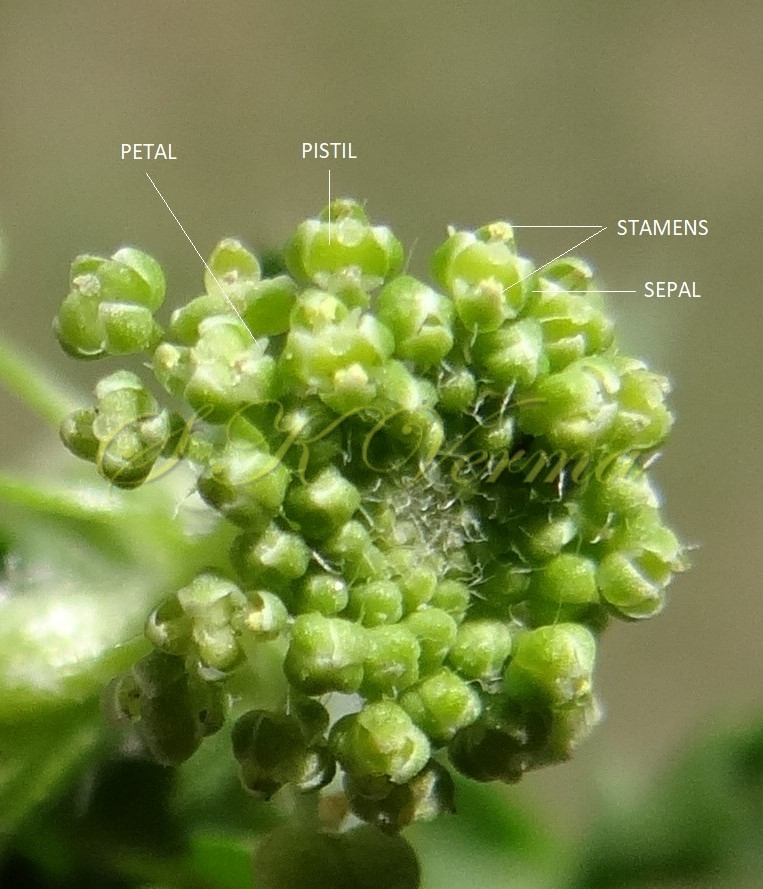
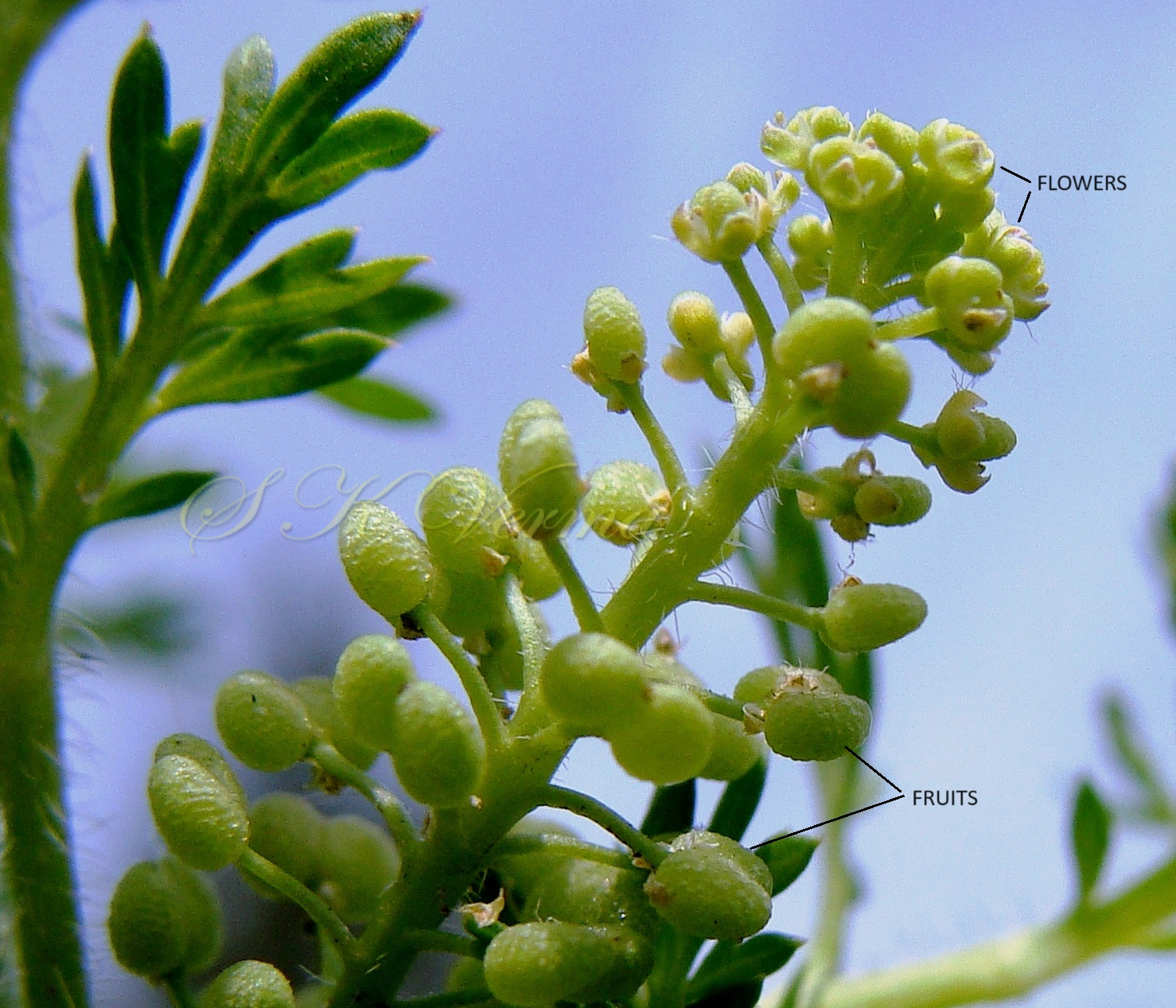
Annual or perennial herbs, often much branched. Leaves usually linear or elliptic, entire, toothed or pinnatifid; lower often petiolate, upper sessile or subsessile. Racemes corymbose, dense, ebracteate. Flowers small, usually white, pedicellate. Sepals 4, short, subequal, oblong, obtuse, glabrous, often green with white margin; inner pair slightly broad, not saccate. Petals 4, small, linear to spathulate, sometimes shorter than sepals, rudimentary or absent. Stamens 6 or by abortion 4 or 2; filaments simple; anthers short, ovoid or suborbicular, obtuse. Nectar glands usually fragmentary, minute, present between the stamen bases. Ovary flat, elliptic with 2 pendulous ovules; style short or absent; stigma capitate. Siliculae ovate, obovate, orbicular or broadly elliptic; apex often notched, laterally flattened; dehiscent, bilocular, valves usually strongly keeled, often slightly winged towards apex, septum narrowly elliptic, membranous, not veined. Seeds generally one in each locule, usually obliquely ovate, brown.
262 species
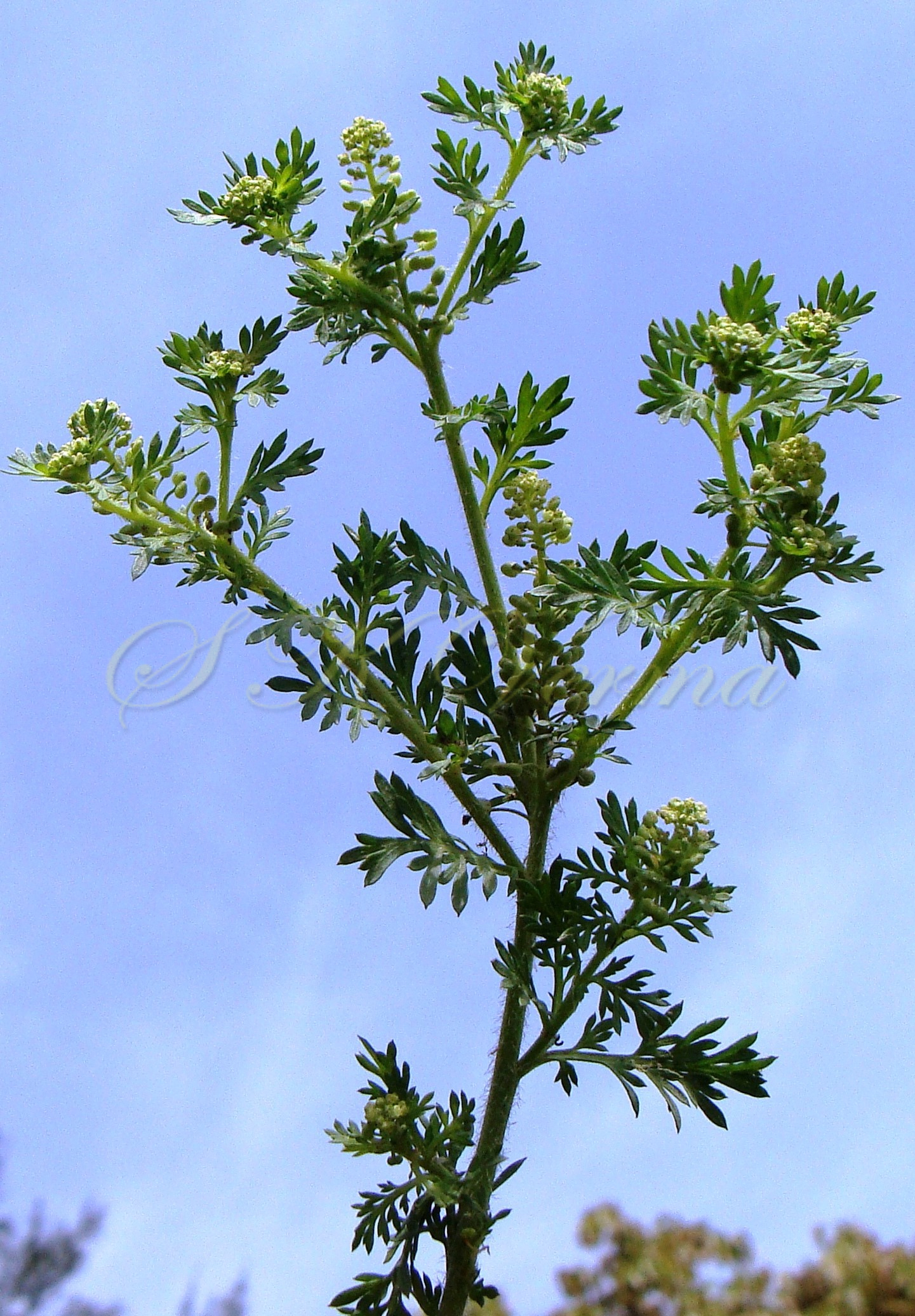
Lepidium didymum
Lepidium didymum
L., Mant. Pl. 1: 92. 1767; Coronopus didymus (L.) Smith, Fl. Brit. 2: 691. 1800; Schulz in Engl. & Prantl, Pflanzenfam. ed. 2, 17b: 412. 1936; Sharma & Kachroo, Fl. Jammu (Illustr.) 2: t. 15. 1983; Dhaliwal & Sharma, Fl. Kullu Dist. 133. 1999; Kaur & Sharma, Fl. Sirmaur 140. 2004; Singh & Sharma, Fl. Chamba Dist. 161. 2006; Fl. China 8: 33. 2001; Fl. Pak. @ eFloras.org; Senebiera didyma (Linn.) Pets., Syn. Pl. 2: 185. 1807; S. pinnatifida DC., Syst. Nat. 2: 144. 1821.
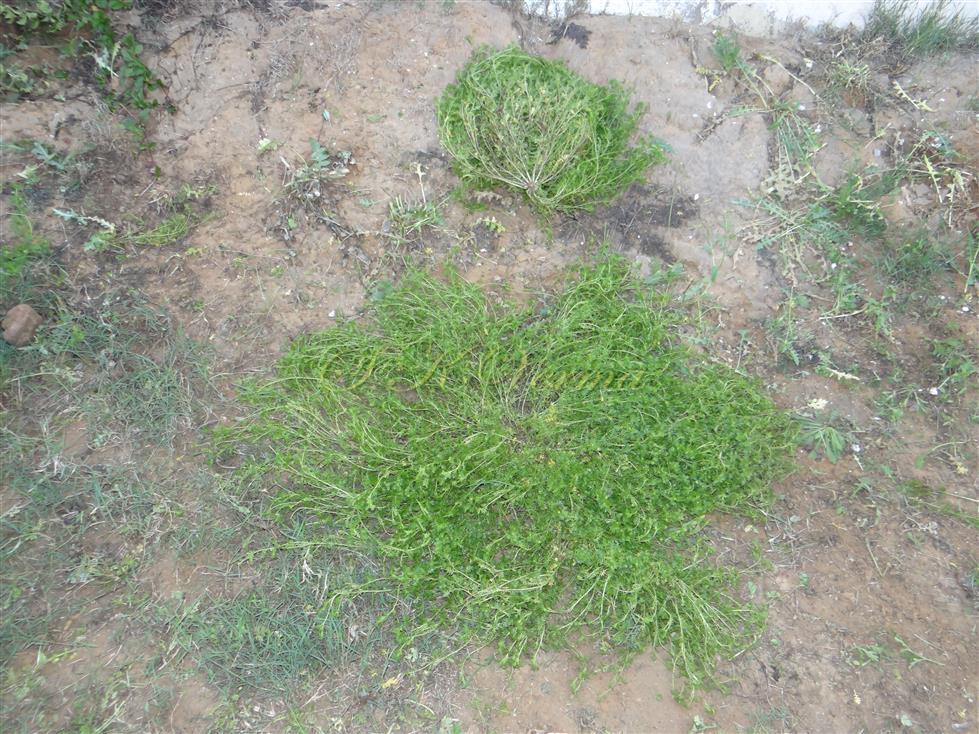
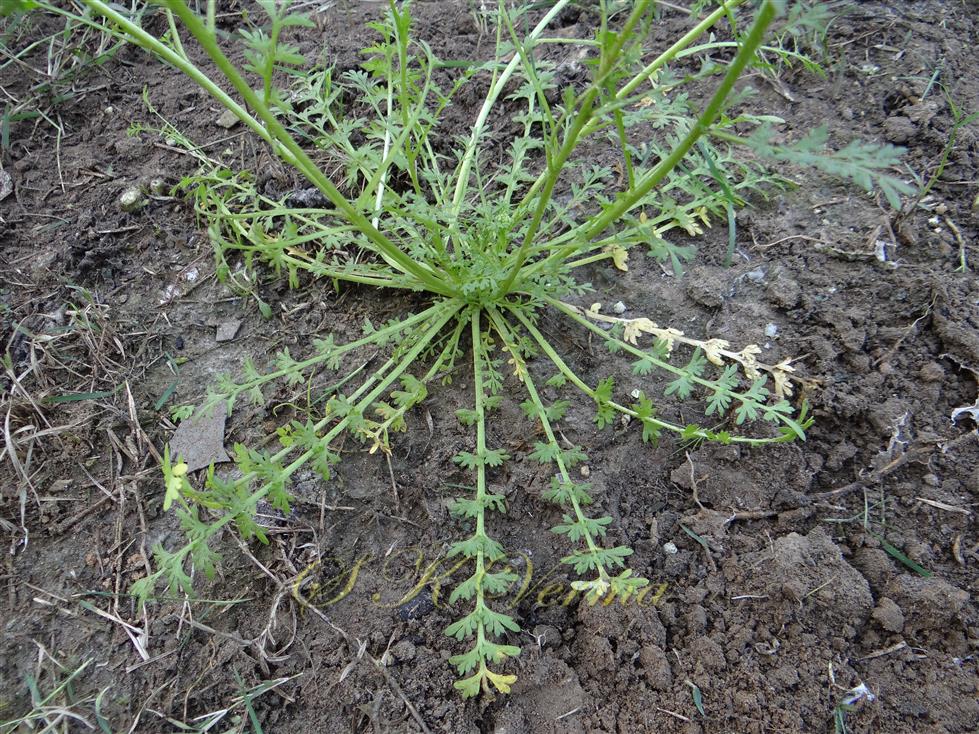
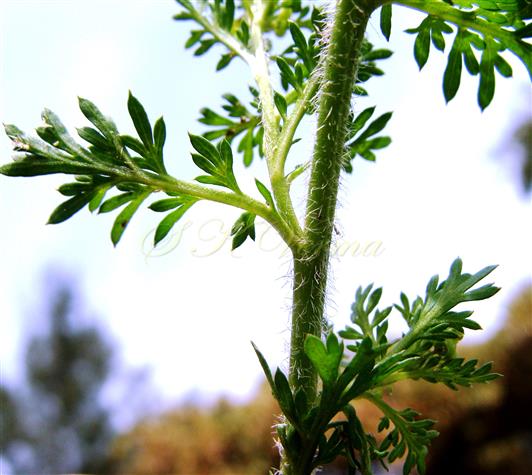
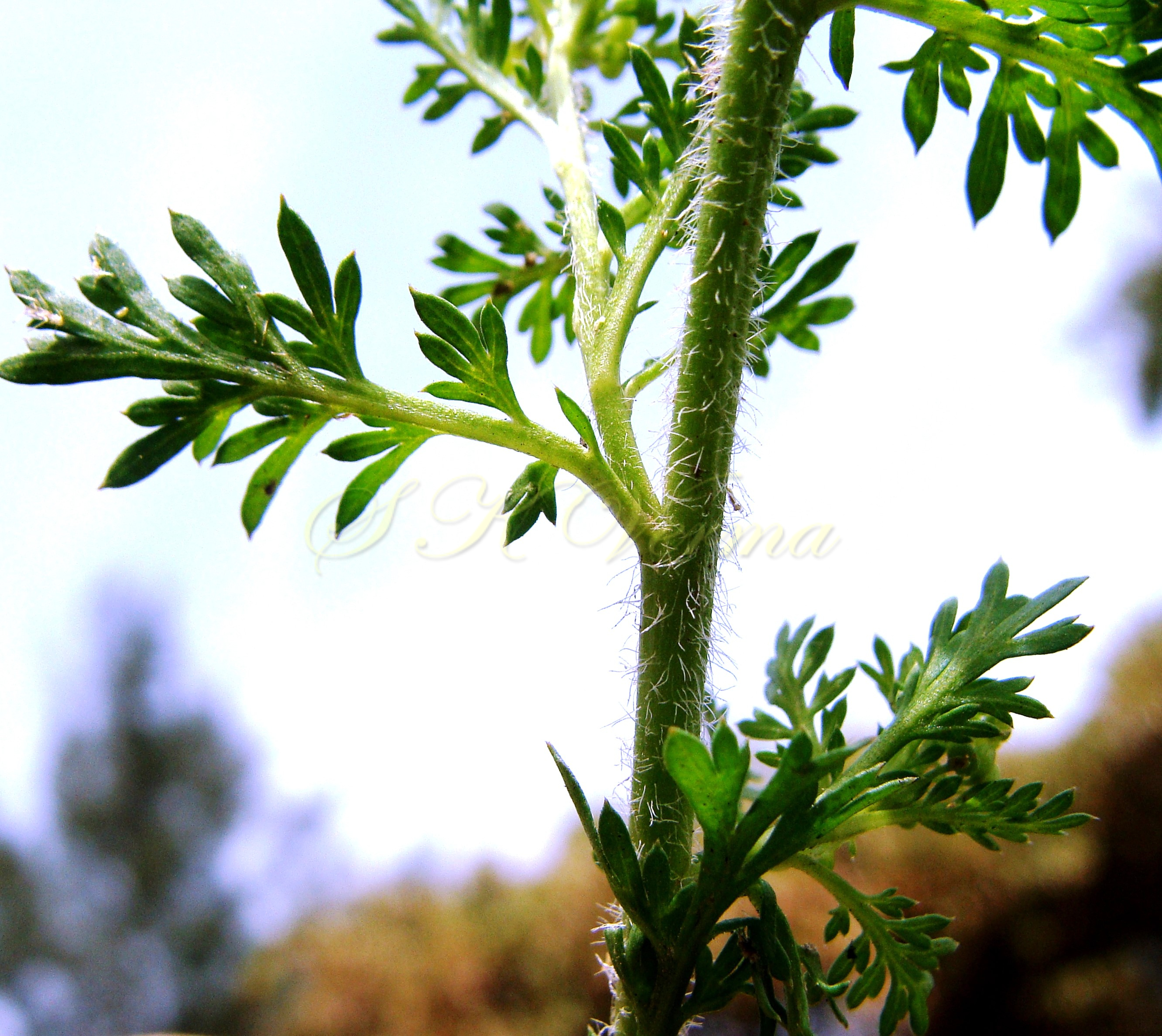
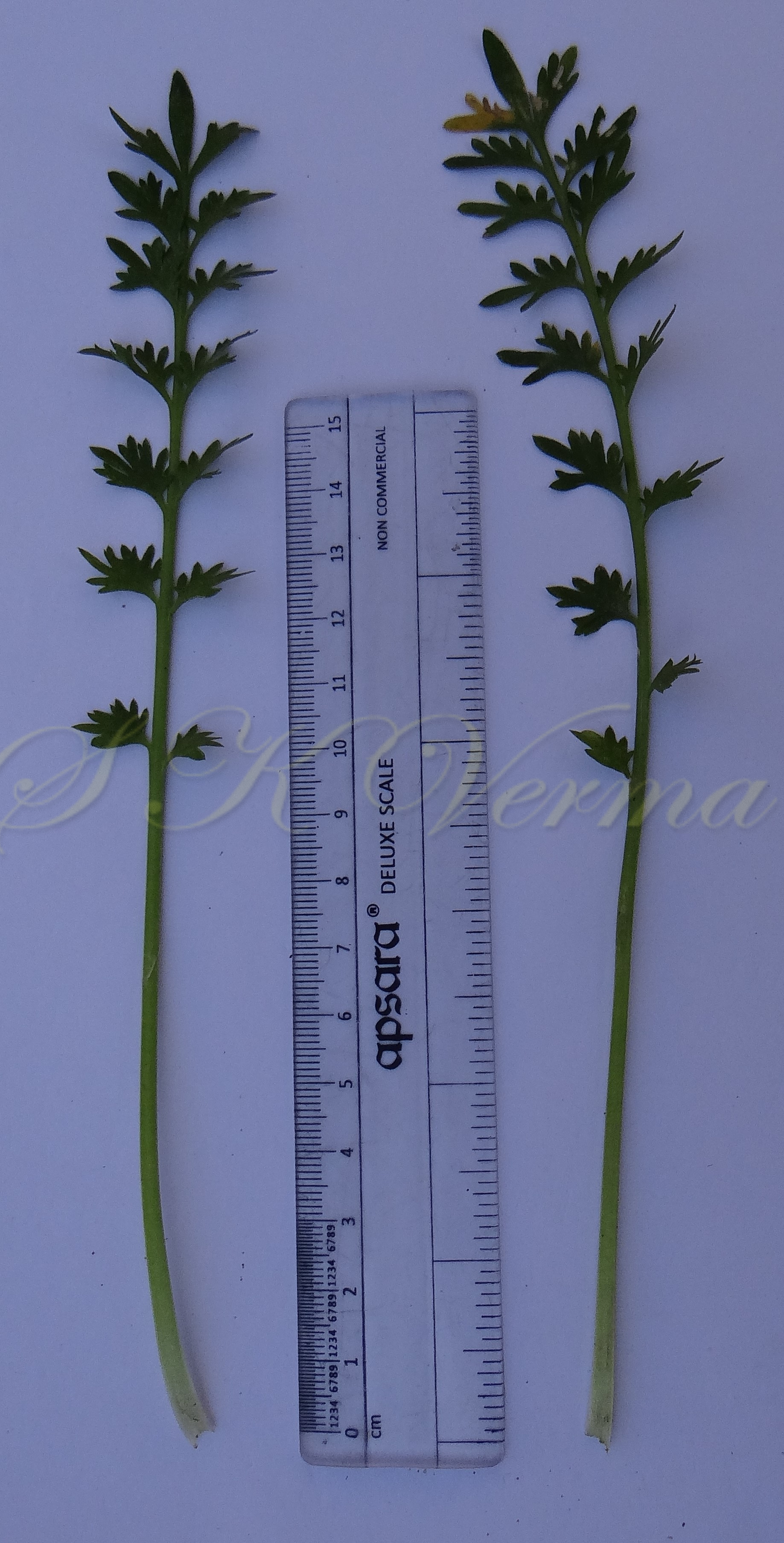
Herbs, annual or rarely biennial, foetid, 10-70 cm tall, pilose with straight trichomes to 1 mm. Stems procumbent or erect, usually several from the base, branched above, single plant covering an area of diameter 130-140 cm. Basal leaves rosulate or not, petiolate (petiole up to 10 cm long), pinnatisect, 4-15(-22) cm (including petiole) long, 6-10-jugate, lateral lobes 6-10 on each side of rachis, variable in size, entire, dentate or incised, acute. Middle and upper cauline leaves similar or 1-2-pinnatifid and 3-5-jugate, 1.5-3.5(-7.5) cm x 0.5-1.2 cm, progressively smaller and less divided upwards, shortly petiolate to subsessile; lobes 4-8 mm long, sessile, lanceolate to oblong or elliptic, entire to serrate or incised or segmented only on one side, pilose. Racemes terminal or lateral, leaf opposed; 30-60 flowered, dense, usually small, up to 8 cm long in fruit, pubescent. Fruiting pedicels slender, filiform, ascending to divaricate or slightly reflexed, straight or recurved, 1.5-2.5(-4) mm long, glabrous or pubescent. Flowers minute, ca. 1 mm across, 1-1.5 mm long. Sepals 4, ovate, ca. 1 mm x 0.5 mm, ascending to spreading, sparsely pilose. Petals 4, white, elliptic to linear, minute, ca. 0.5 mm x 0.2 mm. Stamens 2, median; anthers ovoid, 0.1-0.2 mm. Siliculae shorter than pedicel, 1.3-1.7 mm x 2-3 mm, didymous (bilobed), compressed, emarginate at apex and base; valves subreniform, semicircular or suboblong, reticulate or rugose; style absent, sometimes obsolete, included in apical notch. Seeds oblong, reniform, reddish brown, 1-1.2 mm x 0.7-0.8 mm
Common Names: Swine Cress, Bitter Cress, Lesser Swine Cress, Wart Cress; Jangli Hala (Hindi)






-7947.jpg)









-7947.jpg)


